Interest in alternative fuels is growing, despite low adoption levels currently. BuiltWorlds' research examines some of the factors surrounding the adoption of alternative fuels, and the primary hurdles that companies face when considering making the switch. We've also explored some of the ways that these hurdles can be lowered, such as an increase in federal and private investments, as well as regulation and policy incentives.
To dive deeper into the topic, BuiltWorlds hosted an analyst call to discuss alternative equipment fueling options available on the market. During the call, industry experts Karl Thomas from Optimus Technologies and Richard Romer from Instagrid shared their solutions for low-carbon fuels and portable power systems, respectively. Thomas and Romer fielded questions from audience members, providing some perspectives on alternative fuel adoption, which both agree is a matter of when—not if.
Research Snapshot
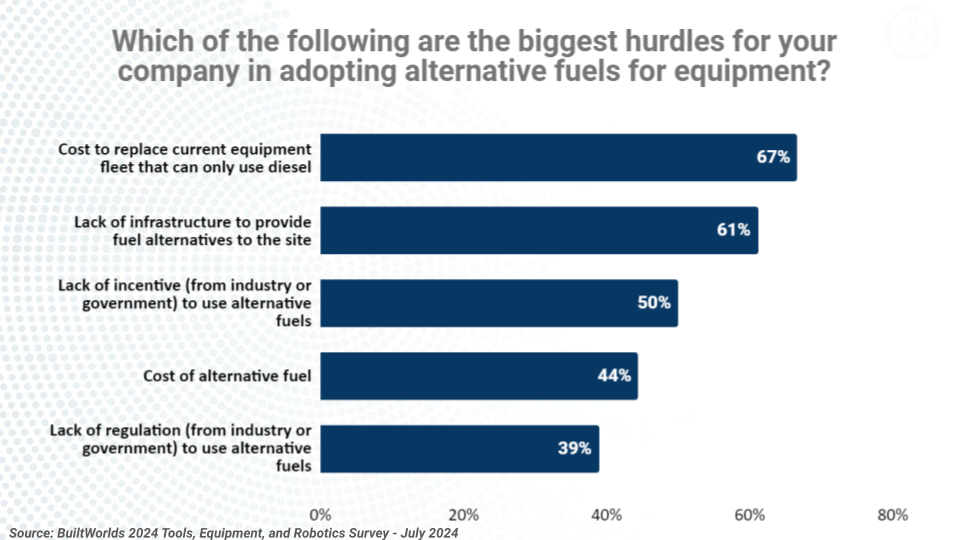
BuiltWorlds’ 2024 Sustainable Jobsites Annual Report indicates that fewer than 15% of surveyed contractors regularly utilize alternative fuels, such as battery or electric-powered methods, or more natural alternatives to diesel, such as sustainable biodiesel. Contractors face various hurdles in adopting alternative fuels - including the high cost of replacing current equipment that can only use diesel, a lack of infrastructure to provide fuel alternatives to jobsites, and the high cost of alternative fuels. Less than a quarter of contractors report using alternative fuels currently, but another quarter of respondents noted that they plan to use alternative fuels within the next 1-3 years.
Key Takeaways
The Major Hurdles: Cost, then Risk
The adoption of alternatives to diesel fuel faces significant challenges, primarily due to the high initial costs and the lack of a cheaper technical solution compared to current fuels. Although the economic benefits of these alternative fuels are promising, they often materialize only in the long term, leading to increased operational costs and added layers of risk for businesses. This risk includes navigating the transition and awaiting long-term results to justify scaling up. Additionally, fear, uncertainty, and doubt regarding new technologies contribute to hesitancy in deployment. To address these challenges, solutions in the space focus on demonstration programs, providing data to prove efficacy, conducting pilot projects, collaborating with trucking companies, and offering 30-day trials to build confidence and demonstrate the practicality of these alternatives.
Navigating the green agenda
We are currently navigating a complex landscape where federal regulations and state-level decarbonization efforts intersect, often overlapping. Companies, especially those with ties to European standards but substantial operations in the U.S., face additional pressures. Despite the political climate, the trajectory towards decarbonization is unmistakably forward. Companies and state and local governments have already implemented regulatory measures that will not become more lenient; for instance, California has banned portable gas-powered generators starting in 2028. There is a growing consensus within the business community about the necessity to decarbonize, recognizing it as both a risk and an opportunity. The shift towards green agendas is inevitable, focusing on the pace rather than the possibility. Key indicators of this transition include the adoption of electric vehicles and the generation and deployment of wind and solar energy. The evolution towards alternative equipment fuels will follow different timelines, driven by regulatory requirements, societal demands, and cost considerations.
Recognizing Benefits and Getting Ahead
There is a significant societal push alongside increasing government regulations driven by a collective awareness of the environmental impacts of the past. The motivations behind this shift can vary, with different entities setting diverse goals and targets. Beyond reducing the carbon footprint, alternative equipment fuels offer additional benefits. For instance, Instagrid provides ergonomic advantages and the convenience of handheld solutions. Engaging users and generating excitement about these alternatives is crucial. Ultimately, adopting these solutions will become a standard business practice, raising the question of whether one is getting ahead of the curve.

Discussion
Be the first to leave a comment.
You must be a member of the BuiltWorlds community to join the discussion.